Tel: +86-574-88167027 E-mail: sales3@beneparts.cn
Views: 45 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2020-12-07 Origin: Site
Vacuum casting is an adaptable and highly dependable casting process that is most often employed to produce prototypes and industrial parts. The process requires a high quality master form. This can be a sample of the industrial part itself, or a model created using 3D printing technology. Once a model/mold has been produced molten metal is drawn into it. Due to the nature of the process there is less turbulence and impurities affecting the finished piece. In regards to vacuum casting our standard parts are OEM pieces, new cast buckets, and new cast rippers.









Precision casting, also known as, Investment Casting, is a process utilizing molds of wax into which molten metal is poured. It is a time-honored method used from ancient times. Today, advanced waxes, refractory materials, and unique alloys are used to produce a various range of qualities and parts. In regards to precision casting we use the technique to produce pieces whose average weight of is between 3 and 50 kilograms, such as bucket teeth, bucket adapters, side cutters, lip protectors, etc.





















Silica sol casting is typically used to produce stainless steel castings. Similar to other casting procedures, Silica sol involves the use of molds and the drawing of metal into them. The process is more expensive than other methods as it produces a smoother surface on the part being produced. In regards to silica sol casting, we produce bucket pins and pieces that weigh less than 3 kilograms and focus especially on parts whose weight is below 1 kilogram and have high surface appearance requirements.
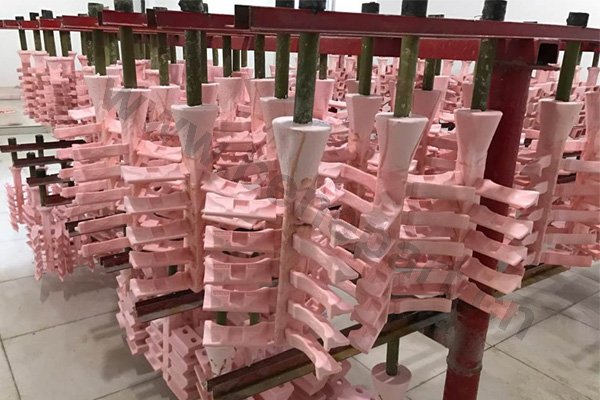
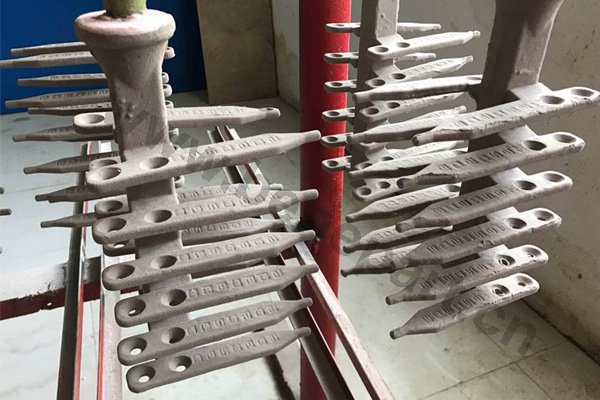
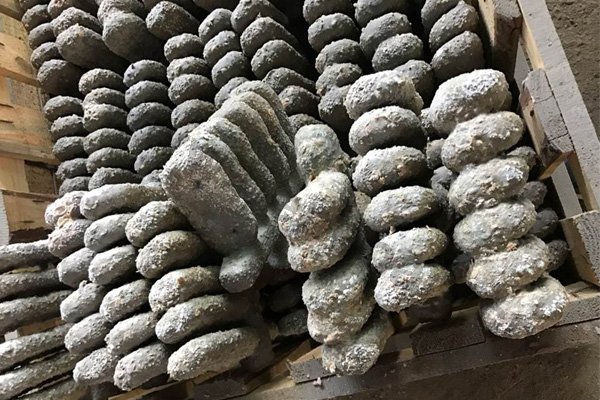
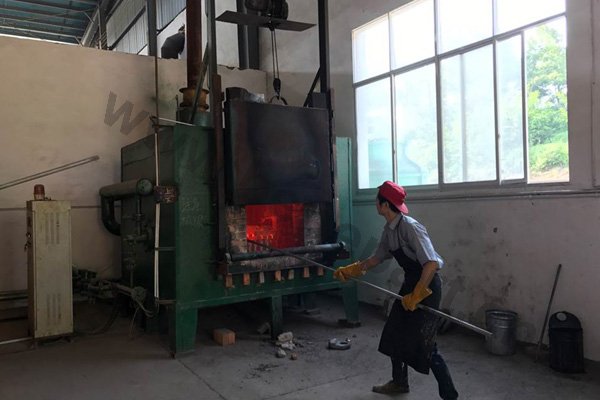
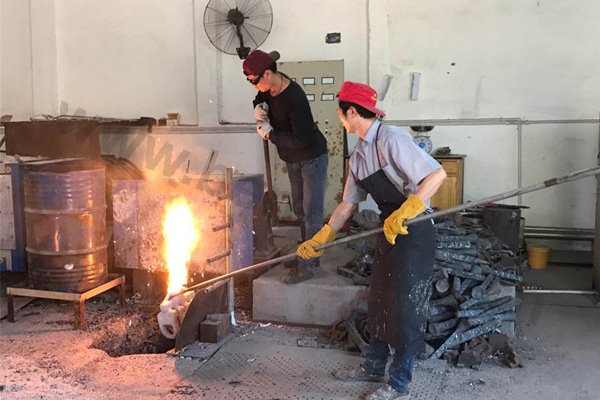
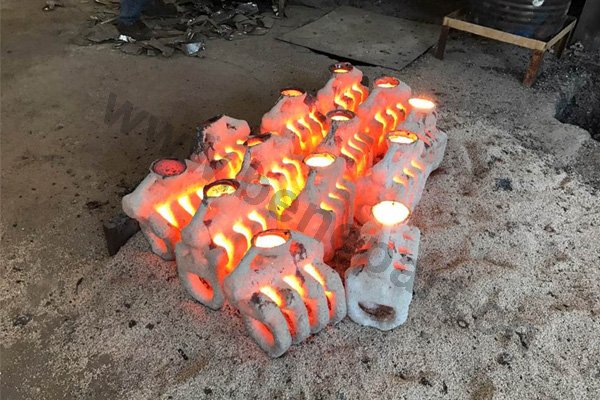






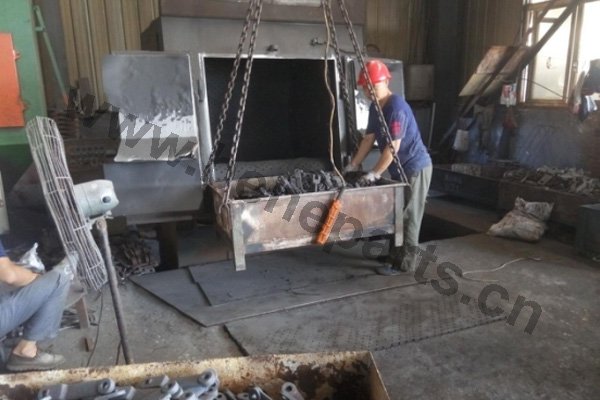
Forging is a metal shaping method using localized compressive forces. Hammers, power hammers, or dies are most commonly used during the forming process. Depending on the piece being formed the forging can be achieved while the metal is cold, warm, or hot. In regards to forging, we construct: chain, forged bucket teeth, and construction machinery parts.
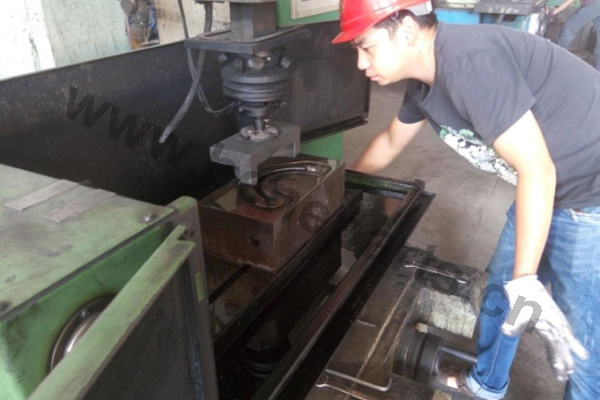
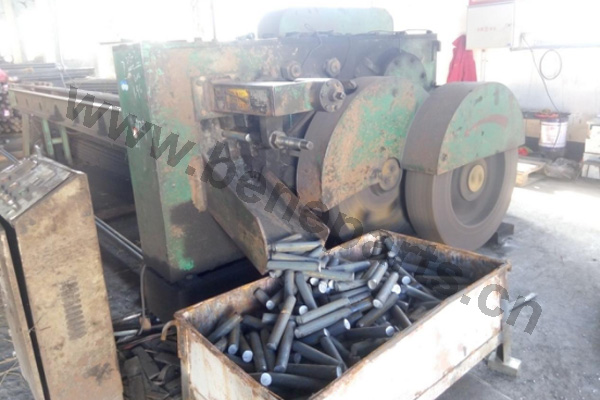
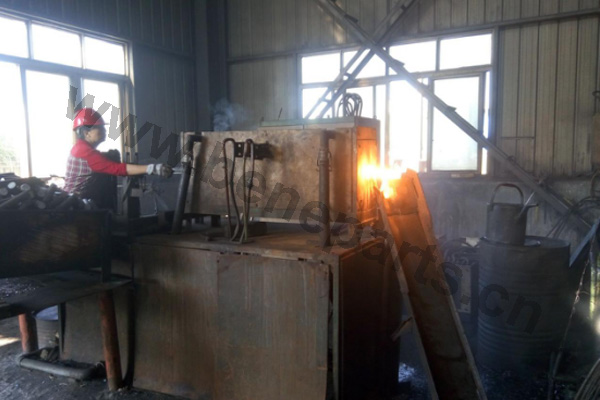
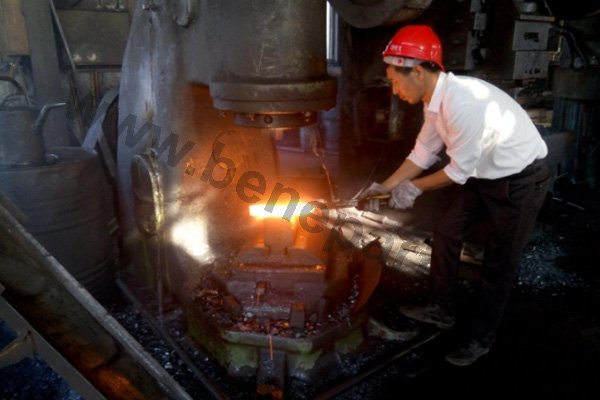
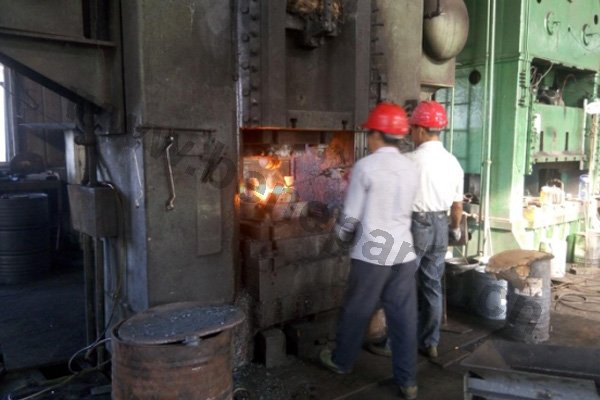
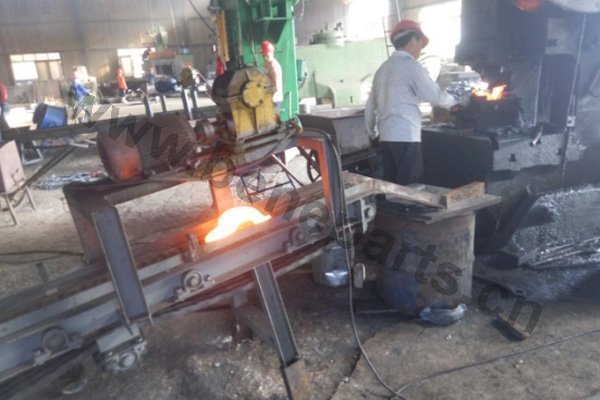
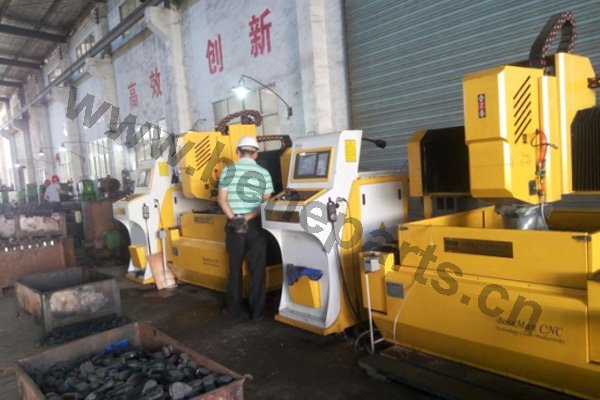
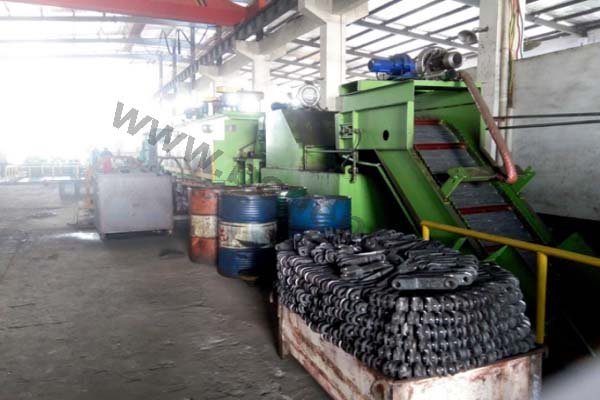
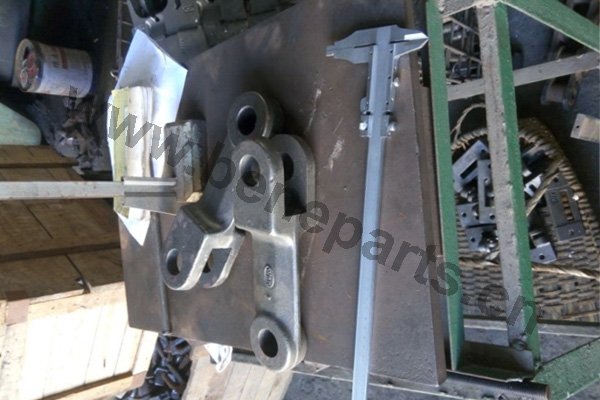
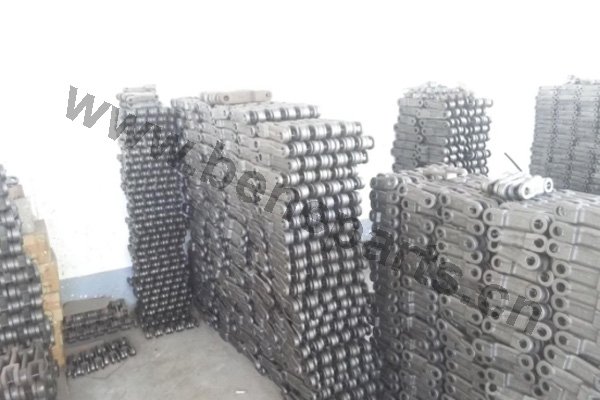












Machining is an unlimited process in which a piece of raw material is cut into an endless variety of shapes and sizes by flame cutting and plasma cutting, milling, the use of saws, drills, punches, etc. In regards to machining, our main products are cutting edges and end bits. Frequently we also will further process these products by casting and/or forging them.
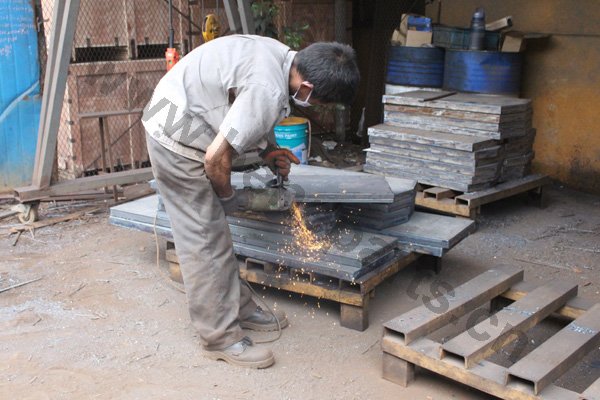
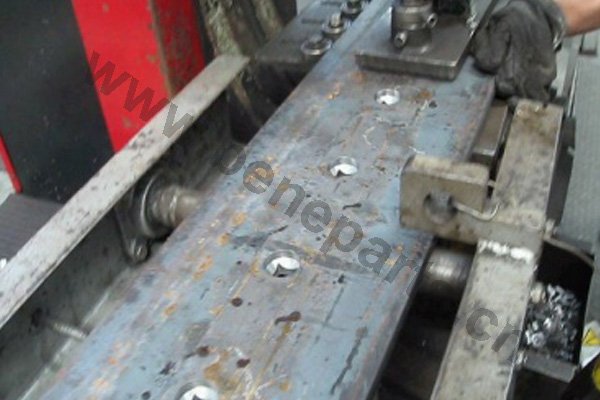
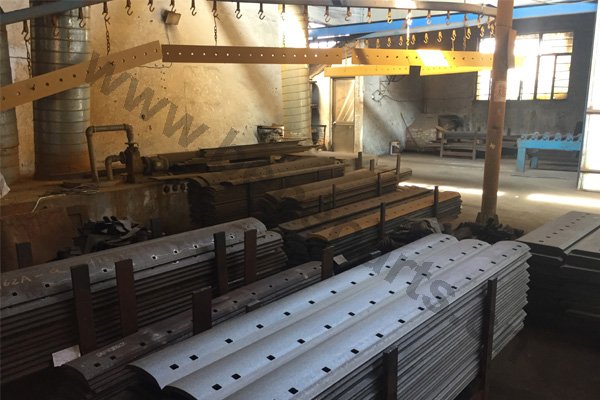
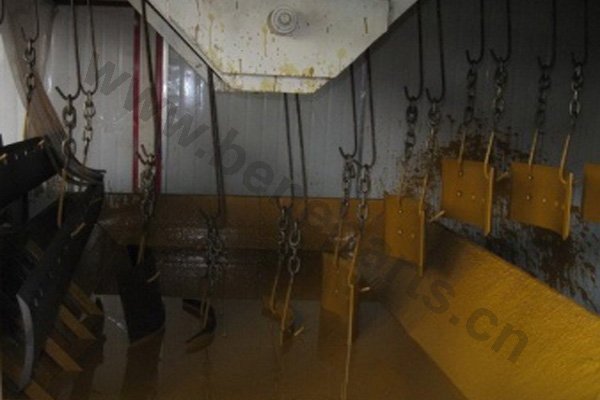
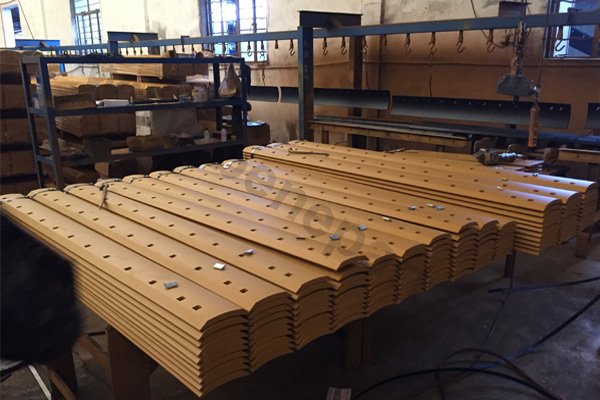





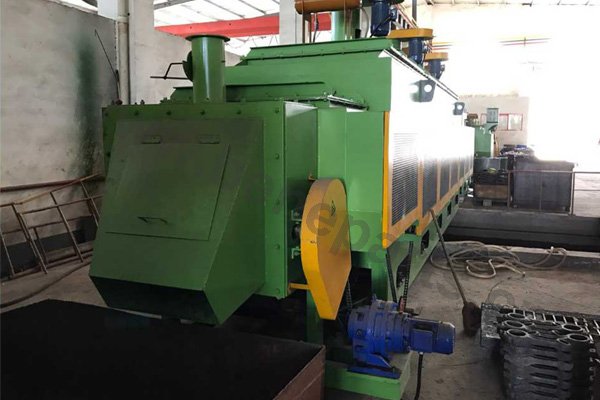
Heat treating (or heat treatment) is a metallurgical process whereby a piece is heated to a precise temperature and then cooled rapidly. This has the effect of group of changing the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of the part undergoing the process.Heat treatment techniques can include annealing, tempering, quenching, and normalizing.
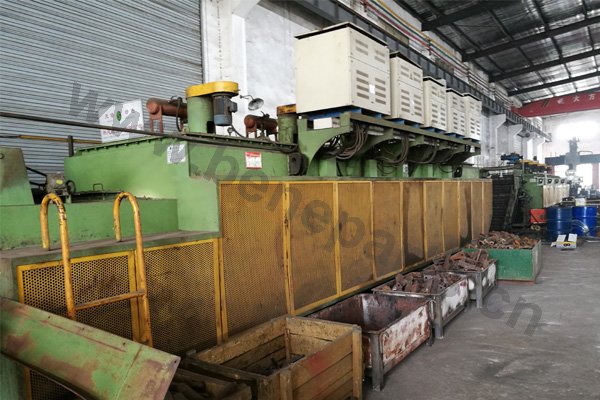
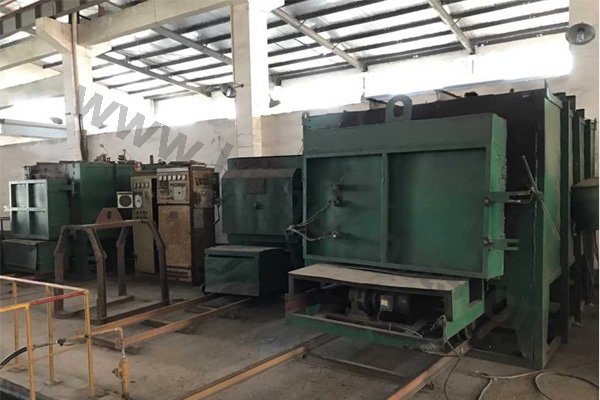
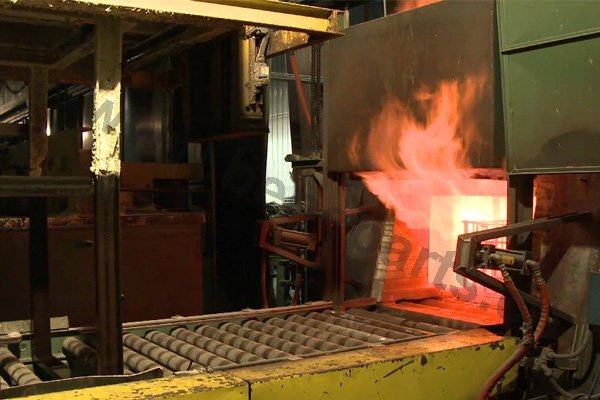
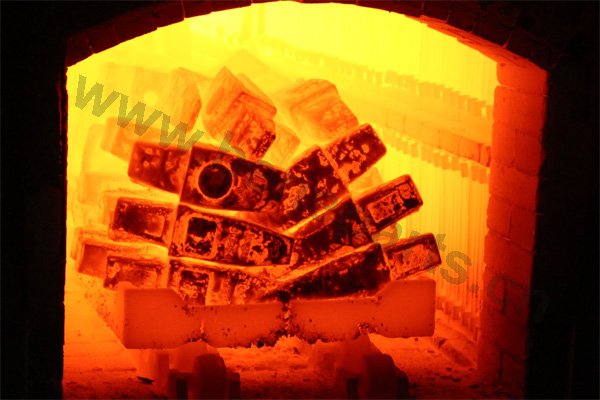






Quality control, or QC for short, is a process by which an outside agency reviews the production steps and all other factors that bear upon items being produced consistently at a high level of precision. Our factory QC program complies to ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems.





